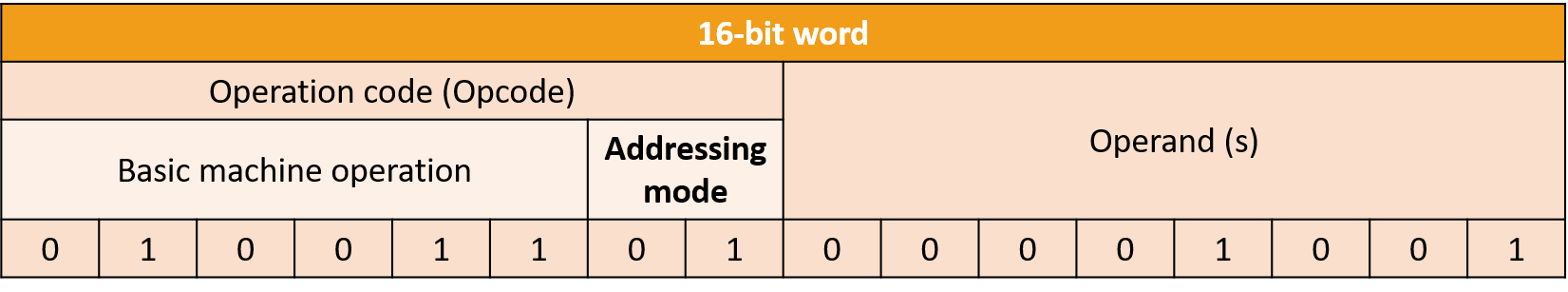
12.3.4.1 explain the principle of memory addressing Addressing modes The term "addressing modes" refers to how the operand of an instruction is defined. The addressing mode defines the rule for interpreting or modifying the address field of an instruction before actually executing the operand. Immediate and direct addressing modes The operation code (opcode) consists of binary digits representing the basic operation such as ADD or LOAD, and a 2-digit code representing the addressing mode.
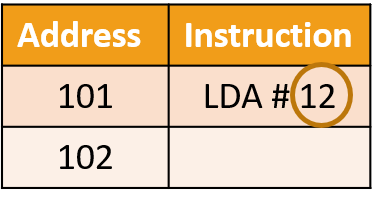
Examples of two addressing modes - immediate (00) and direct (01) addressing. Example, LDA #12 means load the number 12 into the accumulator
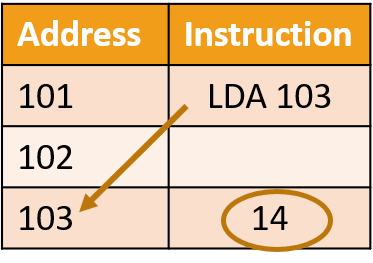
(symbol # means that the immediate addressing mode is being used) In direct addressing, the operand holds the memory address of the value to be operated on. Example, LDA 103 means load the number to the accumulator from location 103
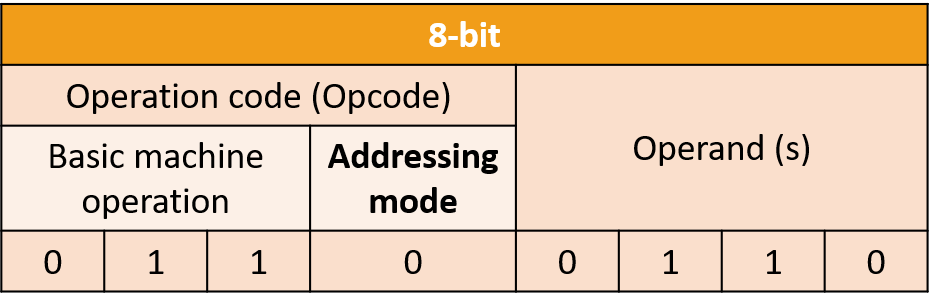
A simple model Consider a simple model in which the addressing mode is included in the bits allocated to the opcode.
Suppose that the code 011 is the ADD mnemonic and addressing mode 0 means immediate addressing, This instruction means "Add the number 6 to the contents of the accumulator". Each assembly language mnemonic corresponds to a binary code, for example
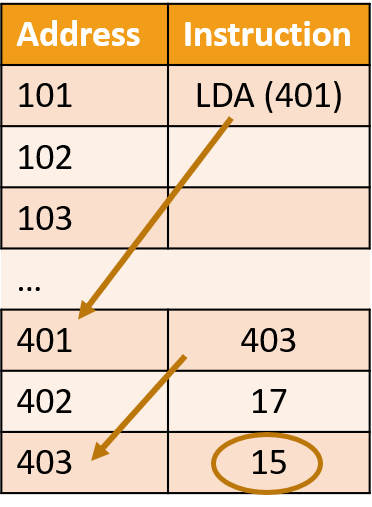
Indirect addressing mode Indirect addressing means that the address of the data is held in an intermediate location so that the address is first ‘looked up’ and then used to locate the data itself. Fetching the value is a two step process: First the indirect address is used to locate an entry into a lookup table (called Vector Table) where the actual address of where the value can be fetched from is stored.
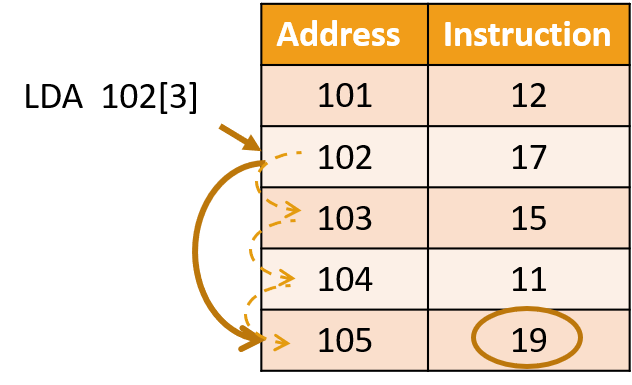
(brackets () means that the indirect addressing mode is being used) Indexed addressing mode Indexed addressing means that the final address for the data is determined by adding an offset to a base address. This memory addressing mode is suitable for storing and accessing values stored in arrays. Arrays are often stored in memory as a block of consecutive memory locations. The array has a base address, which is the location of the first element, then an index is used, which adds an offset to the base address to get the specified element in the array.
Questions:
Exercises: Ex. 1. Match the addressing mode with its description Ex. 2
Exam questions:
| |
|
| |
| Просмотров: 5499 | | |
| Всего комментариев: 0 | |