11.1.2.1 explain the difference between the terms security, privacy, and data integrity
12.1.2.1 describe protection measures for data and computer systems such as physical risks, firewalls, encryption, biometrics
Information security. Data protection measures.
Computer security is the preservation of computing systems and the information that they save and / or retrieve.
Information security skills are currently required by all users.
Only 10% of security measures are technical, and the remaining 90% depend on how much the user cares about the security of their data.
Every user of a computer or mobile device should be able to grasp how to keep their computer, devices, and data secure. Computer security is everyone’s responsibility.
Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption
Cyber security: the use of technology, working practices and precautions designed to protect networks, computers, programs, and data from attack, damage or unauthorised access.
Core Principles of Cyber Security
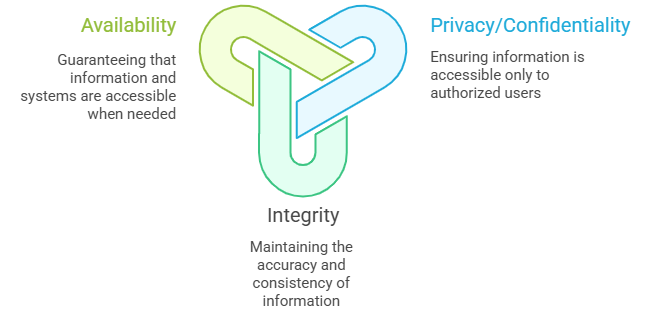
Privacy/Confidentiality – information that should be available only to authorized users.
Integrity means that information cannot be lost or changed from its original state.
Availability – information and systems must always be available to authorised users when needed.
A weakened computer is a threat to everyone.
A hacked computer can be used to do the following:
- Record keystrokes and steal passwords
- Send spam and phishing emails
- Harvest and sell email addresses and passwords
- Gain access to restricted or personal information on your computer, or on other systems that you have access to
- Infect other systems with viruses and other malware
- Conceal programs that launch attacks on other computers
- Illegally disseminate music, movies and software
- Distribute child pornography
- Produce great volumes of traffic, slowing down the whole system
- A weakened computer can be utilised for all kinds of harmful purposes.
Many internet security hazards can be prevented.
Some of the ways computer users can protect themselves against security breaches:
- Use strong, ambiguous passwords that can’t be easily predicted, and keep them secret.
- Ensure that your computer, devices and applications are updated with the latest version of the operating system in question.
- Ensure that your computer is secured with up-to-date antivirus and anti-spyware software.
- Ignore unknown or unsolicited links and attachments. Don’t download unfamiliar files or programs onto your computer or other devices.
- Remember that data, especially passwords transmitted through typical wireless connections, is very easy for hackers to capture.
- Look for ‘https’ in the URL before you input any confidential information or a password. The added s in https means secure, and guarantees a degree of protection not afforded by the standard http markup.
- Avoid using normal, unencrypted e-mail and unencrypted Instant Messaging if you’re concerned about confidentiality.
Consequences for Security Violations
- Risk to both the security and the integrity of personal or confidential information
- Identity theft
- Data corruption or destruction
- Unavailability of critical information in an emergency
- Loss of valuable business information
Sourse: https://teachcomputerscience.com
Topics of the lesson
Physical risks
Firewalls
Encryption
Biometrics
Questions:
- Give definition for terms "security", "privacy" and "integrity".
- Define the key difference between “security” and “privacy”/ between “integrity” and “privacy”.
- Provide examples which demonstrate "security", "privacy" or "integrity".
Exercises:
Ex. 1
Ex. 2 (Author - Litvinova Olga - NIS Pavlodar)
Ex. 3 Solve a Puzzle "Cyber security"
Exam questions:
Question. What are some ways an employee can do to secure personal data? (Marks: 2)
- Answer.
- Encrypt or password protect any personal data held electronically (1)
- Dispose properly documents containing personal data that are no longer needed (1)
- Regularly back up information on computer systems and keep the back ups in a separate location (1)
Question. What are some measures an organisation can take to secure personal data? (Marks: 2)
- Answer.
- Install firewalls and virus-checking software on employees’ computers (1)
- Secure portable computing devices when not in use by locking them up or attaching them to a fixture by a security cable (1)
- Limit employee access to sensitive and confidential documents on a need-to-know basis(1)
| 