|
11.2.1.6 use data flow diagrams (DFD) to input, process, store, and output data in computing systems Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
A data flow diagram (DFD) illustrates how data is processed by a system in terms of inputs and outputs. As its name indicates its focus is on the flow of information, where data comes from, where it goes, and how it gets stored. DFD Symbols There are four basic symbols that are used to represent a data-flow diagram. External Entity An external entity is a person, department, outside organization, or other information system that provides data to the system or receives outputs from the system. They either supply data or receive data
Notation A rectangle represents an external entity
Examples:
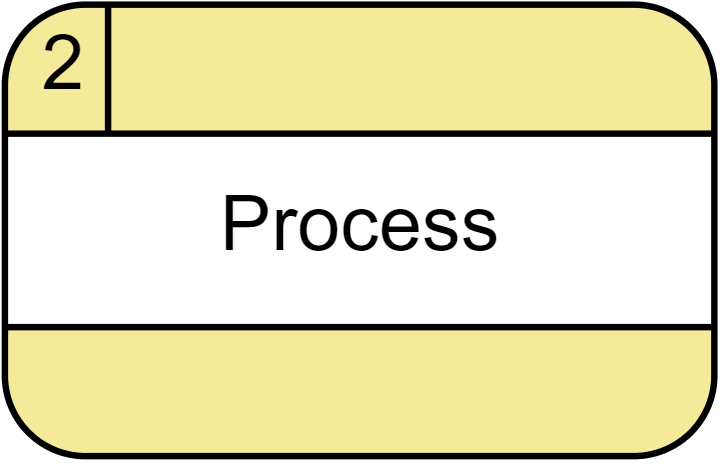
Process A process receives input data, processes it, and produces output with a different content or form. Every process has a name that identifies the function it performs. The name consists of a verb, followed by a singular noun. Notation A rounded rectangle represents a process
Examples:
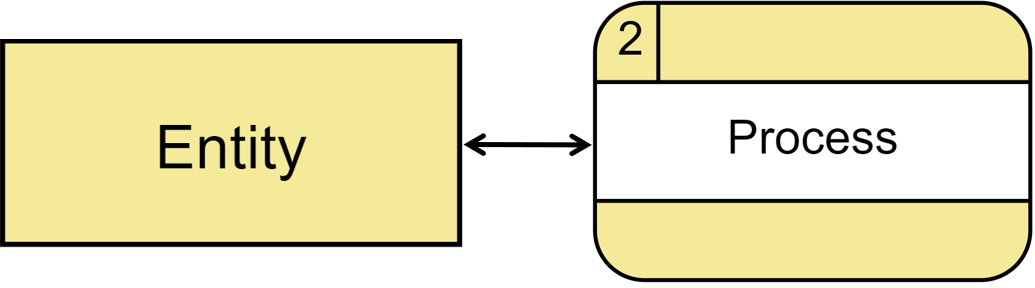
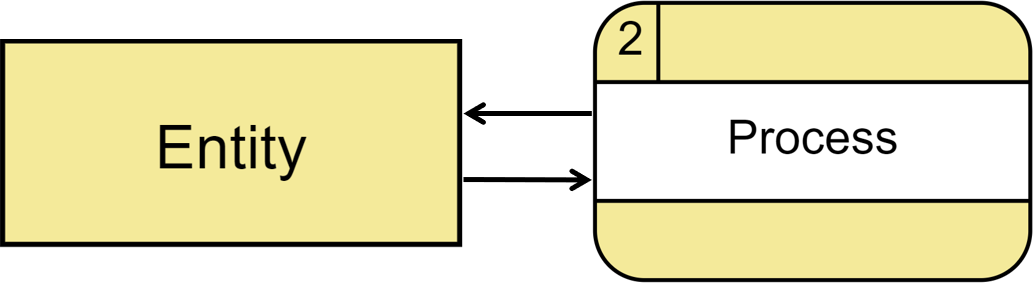
Data Flow Data flow is the inputs and outputs of processes. A data flow may represent a single data element such as the Customer ID or it can represent a set of data elements (or a data structure). Notation Straight lines with incoming arrows are input data flow
Examples:
Data Store A data store is used in a data-flow diagram to represent a situation when the system must retain data because one or more processes need to use the stored data at a later time.
Notation Data can be written into the data store, which is depicted by an outgoing arrow
Examples:
DFD has often been used for the following reasons:
Mistakes in DFD
Other logical mistakes:
More details in the source www.visual-paradigm.com Advantages of DFD
Disadvantages of DFD
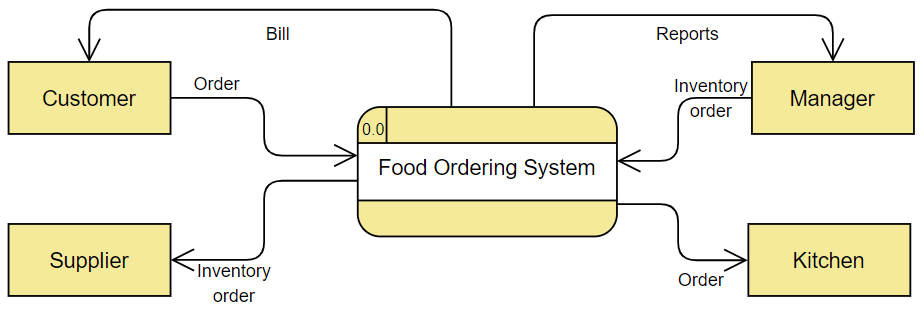
Source: www.geeksforgeeks.org Levels of DFD Level 0 It is also known as a context diagram. It’s designed to be an abstract view, showing the system as a single process with its relationship to external entities.
Examples 1 - Food Ordering System
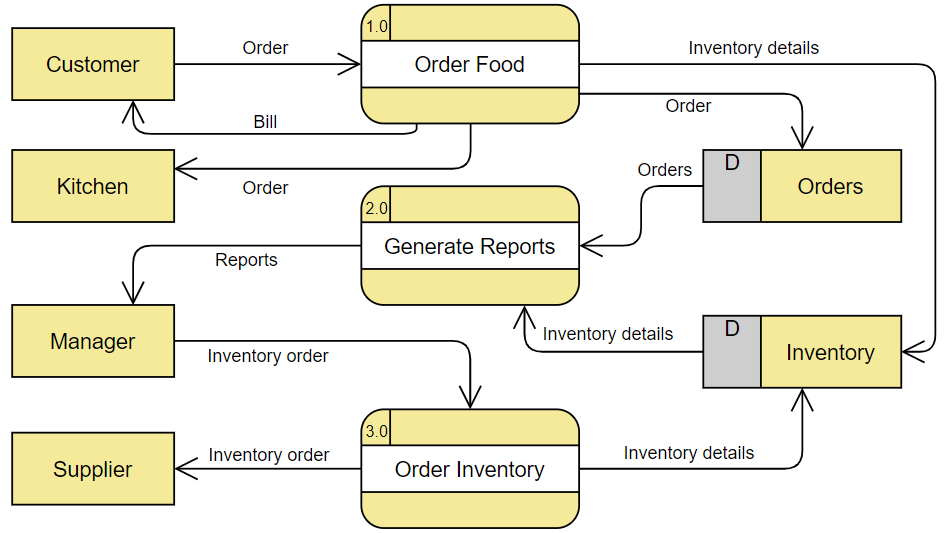
Level 1 In 1-level DFD, the context diagram is decomposed into multiple processes. In this level, we highlight the main functions of the system and break down the high-level process of 0-level DFD into subprocesses further to represent details of the processing activities. Examples 1 - Food Ordering System
Level 2 If a process with a lot of data flow linking between a few external entities, we could first extract that particular process and the associated external entities into a separate diagram similar to a context diagram, before refining the process into a separate level of DFD; and by this way you can ensure the consistency between them much easier. Example 2 - Customer Service System Questions: Ex. 1 (Author: Litvinova Olga - CS teacher of NIS Pavlodar) Exercises: Ex. 2 Ex. 3 Distribute correct and incorrect DFD fragments. Ex. 4 (Author: Litvinova Olga - CS teacher of NIS Pavlodar) Exam questions:
| |||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Просмотров: 21742 | | | |||||||||||||||||||
| Всего комментариев: 0 | |