12.5.1.2 create a simple expert system
Expert system on declarative language
An expert system is a computer system that emulates the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Key terms used in Expert systems
A fact is a basic assertion about a specific relationship or property in the problem domain.
A fact is a small portion of important information. Facts on their own are of very limited use.
A rule is a conditional statement that defines a relationship based on other facts or rules.
A query is a question asked to the system to determine if certain facts or rules are satisfied.
Prolog
Prolog (Programming in Logic) is a high-level language rooted in formal logic. It’s particularly known for its use in artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and computational linguistics.
Key Concepts of Prolog:
-
Facts: These are basic assertions about some relationships or properties. They state unconditionally true things. For example:
parent(john, mary).
-
Rules: These are conditional assertions that describe relationships between facts. They are defined using implications. For example:
grandparent(X, Y) :- parent(X, Z), parent(Z, Y).
This rule states that X is a grandparent of Y if X is a parent of Z and Z is a parent of Y.
-
Queries: A query is a way to ask the system whether certain conditions are met based on the facts and rules provided. For example:
?- grandparent(john, Y).
This asks Prolog to find all Y such that John is the grandparent of Y.
-
Backtracking: Prolog uses a mechanism called backtracking to systematically search through possible solutions to queries. If Prolog hits a dead end while solving a problem, it goes back and tries a different path.
Note: pay attention to the syntax of the language
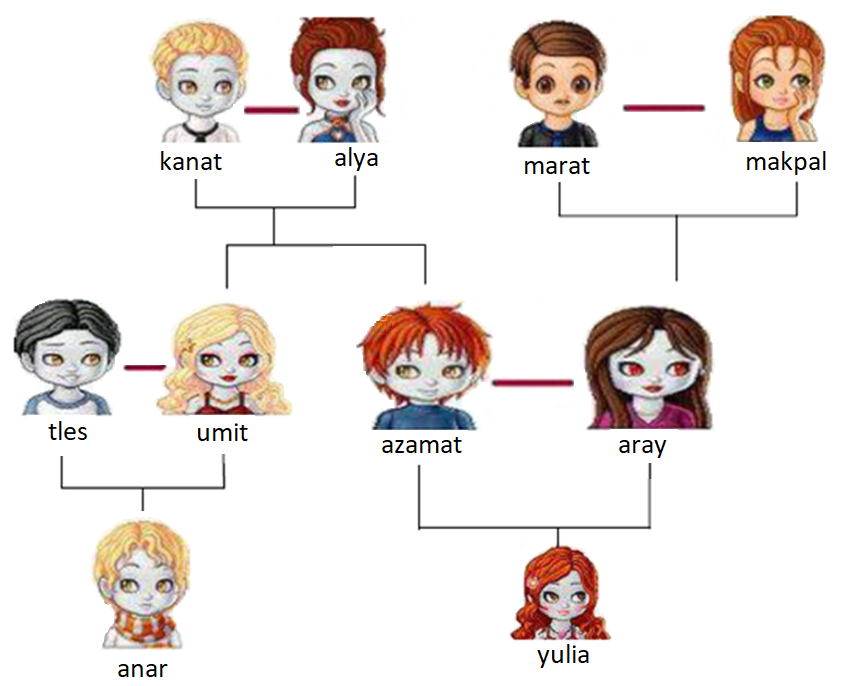
Task: Create an expert system for the next family tree
https://swish.swi-prolog.org/
Facts
male(kanat).
male(azamat).
...
female(alya).
female(umit).
...
parent(kanat, umit).
parent(kanat, azamat).
...
Rules
father(X, Y):-parent(X, Y), male(X).
...
Complete the task.
Queries:
male(kanat). //True
male(alya). //False
parent(kanat, umit). //true
parent(marat, umit). //false
father(kanat, X). // X = umit X = azamat
Additionally, Learn Prolog Now!
Questions:
- Give definitions for the terms "expert system", "fact" and "rule".
- Explain features of the declarative programming paradigm.
Exercises:
Ex. 1 "Create an expert system in Prolog"
Write an expert system for the next family tree:

Create five queries.
Ex. 2 "Analyze Prolog program"
Answer the questions and fill in the blanks using the source.

Ex. 3
Answer the questions and fill in the blanks using the source.

Exam questions:
Worksheet
| 


